Το πρόγραμμα ΠΕΔΙΟΝ 24 έχει σκοπό τη συνεχή καταγραφή (σε 24ωρη βάση) των επιπέδων της ηλεκτρομαγνητικής ακτινοβολίας σε διάφορες περιοχές της Ελλάδας και τη δημοσίευση των αποτελεσμάτων στο διαδίκτυο. Το σύστημα ΠΕΔΙΟΝ 24 αποτελείται από σταθμούς μέτρησης των επιπέδων της ηλεκτρομαγνητικής ακτινοβολίας, εγκατεστημένους σε διάφορες περιοχές. Οι σταθμοί μέτρησης είναι εφοδιασμένοι με ειδικά, πιστοποιημένα όργανα μέτρησης ηλεκτρικού πεδίου τα οποία κάθε 6 λεπτά καταγράφουν και αποθηκεύουν στη μνήμη τους μία τιμή έντασης ηλεκτρικού πεδίου. Κάθε 24 ώρες οι σταθμοί μέτρησης επικοινωνούν μέσω του δικτύου GSM με το κέντρο διαχείρισης και αποστέλλουν τα δεδομένα στον κεντρικό εξυπηρετητή στον οποίο γίνεται η επεξεργασία τους και η δημοσίευσή τους στο διαδίκτυο.
Οι σταθμοί μέτρησης του προγράμματος ΠΕΔΙΟΝ 24 καταγράφουν σε 24ωρη βάση τις τιμές έντασης του ηλεκτρομαγνητικού πεδίου στην περιοχή συχνοτήτων από 100kHz έως 7GHz. Στην περιοχή αυτή του ηλεκτρομαγνητικού φάσματος λειτουργούν οι περισσότερες ασύρματες τηλεπικοινωνιακές υπηρεσίες στη χώρα μας. Συγκεκριμένα, στη ζώνη συχνοτήτων αυτή εκπέμπουν οι κεραίες ραδιοφωνίας, τηλεόρασης, κινητής τηλεφωνίας (2G,3G,4G), ασύρματων δικτύων (Wi-Fi) και άλλων υπηρεσιών. Έτσι το πρόγραμμα ΠΕΔΙΟΝ 24 παρέχει μία ολοκληρωμένη ενημέρωση για τα επίπεδα της ηλεκτρομαγνητικής ακτινοβολίας που προκύπτει από τις προαναφερθείσες πηγές.
Το πρόγραμμα ΠΕΔΙΟΝ 24 υλοποιήθηκε από το Εργαστήριο Κινητών Ραδιοεπικοινωνιών του Εθνικού Μετσόβιου Πολυτεχνείου, το Εργαστήριο Ραδιοεπικοινωνιών του Αριστοτελείου Πανεπιστημίου Θεσσαλονίκης, το Εργαστήριο Συστημάτων Υπολογιστών & Επικοινωνιών του Πανεπιστημίου Αιγαίου, το Εργαστήριο Διαδικτυακών και Τηλεπικοινωνιακών Συστημάτων, Υπηρεσιών και Ασφάλειας του Πανεπιστημίου Πειραιά. Τα 4 ελληνικά Πανεπιστήμια διαχειρίζονται καθημερινά το πρόγραμμα Πεδίον 24 και είναι υπεύθυνοι για την έγκυρη και έγκαιρη ενημέρωση του κοινού.
Πρόκειται για ταλαντώσεις ηλεκτρικών και μαγνητικών πεδίων που διαδίδονται ως κύματα με την ταχύτητα του φωτός. Η ηλεκτρομαγνητική ακτινοβολία μας είναι γνωστή στο φυσικό και τεχνητό περιβάλλον με διάφορες μορφές. Η υπέρυθρη ακτινοβολία, το ορατό φως, η υπεριώδης ακτινοβολία, οι ακτίνες Χ αποτελούν μέρος του ηλεκτρομαγνητικού φάσματος όπως και οι συχνότητες της ραδιοφωνίας και της τηλεόρασης, τα μικροκύματα και τα ηλεκτρικά και μαγνητικά πεδία του ηλεκτρικού σιδηροδρόμου και των γραμμών μεταφοράς ρεύματος της ΔΕΗ. Όσον αφορά την ακτινοβολία της κινητής τηλεφωνίας, αποτελεί την ηλεκτρομαγνητική ακτινοβολία στην περιοχή συχνοτήτων 900 MHz και 1800 MHz. Από φυσικής άποψης, οι διάφορες αυτές ακτινοβολίες διαφέρουν κατά τη συχνότητα και την ενέργεια τους.
Με βάση τη συχνότητα η εκπεμπόμενη ακτινοβολία χωρίζεται σε “μη ιοντίζουσα” και “ιοντίζουσα”.
Η ιοντίζουσα ακτινοβολία χαρακτηρίζεται από πολύ υψηλές συχνότητες εκπομπής και έχει την ιδιότητα να προκαλεί ιοντισμό των ατόμων (δηλαδή να εκδιώξει ένα ηλεκτρόνιο από ένα άτομο). Για το λόγο αυτό η ιοντίζουσα ακτινοβολία μπορεί να προκαλέσει βλάβες σε κύτταρα, ιστούς και γενικότερα σε βιολογικούς οργανισμούς. Παραδείγματα ιοντίζουσας ακτινοβολίας είναι οι ακτίνες Χ και οι ακτίνες Γ που εκπέμπονται από ραδιενεργά υλικά. Αντιθέτως, η μη ιοντίζουσα ακτινοβολία δεν προκαλεί ιοντισμό των ατόμων. Παραδείγματα μη ιοντίζουσας ακτινοβολίας είναι το ορατό φως, η υπεριώδης ακτινοβολία, το υπέρυθρο φως, τα ραδιοκύματα και τα μικροκύματα. Οι εκπομπές από κεραίες ραδιοφωνίας, τηλεόρασης, κινητής τηλεφωνίας, δορυφορικών συστημάτων και ραντάρ δηλαδή το σύνολο της ηλεκτρομαγνητικής ακτινοβολίας ραδιοσυχνοτήτων αποτελεί μη ιοντίζουσα ακτινοβολία. Το σχήμα που ακολουθεί παρουσιάζει το ηλεκτρομαγνητικό φάσμα:
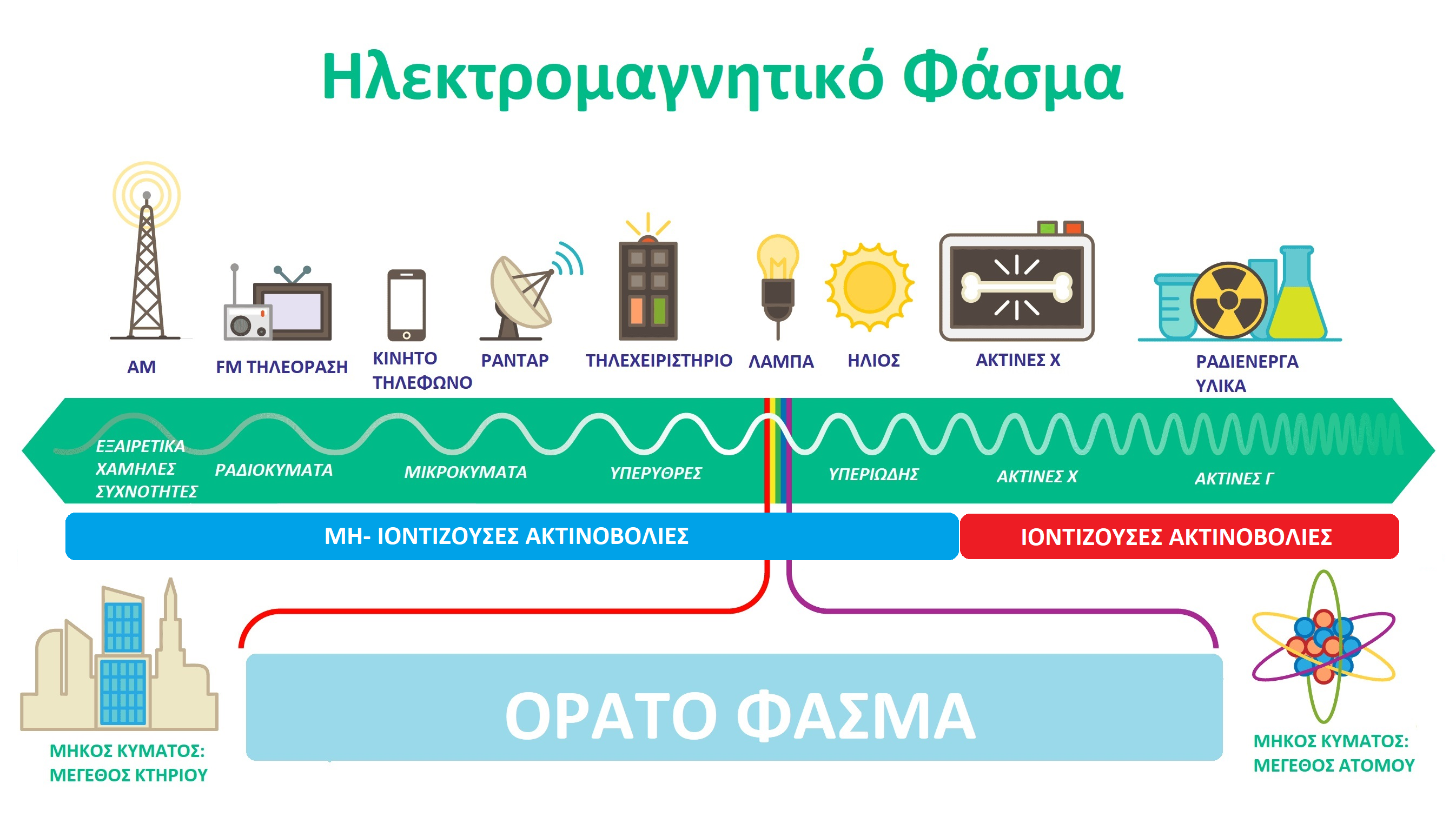
Σε σχέση με την ενέργεια που μεταφέρουν, τα ηλεκτρομαγνητικά κύματα μπορούν να περιγραφούν από τα ακόλουθα μεγέθη:
– Ένταση ηλεκτρικού πεδίου Ε (μονάδα μέτρησης: Βολτ ανά μέτρο – V/m)
– Ένταση μαγνητικού πεδίου Η (μονάδα μέτρησης: Αμπέρ ανά μέτρο – Α/m)
– Πυκνότητα Ροής Ισχύος S (μονάδα μέτρησης: Βαττ ανά τετραγωνικό μέτρο – W/m2)
Στην περιοχή των ραδιοσυχνοτήτων το βασικό μέγεθος που χαρακτηρίζει τα ηλεκτρομαγνητικά πεδία είναι η ένταση του ηλεκτρικού πεδίου η οποία και καταγράφεται στα πλαίσια του προγράμματος ΠΕΔΙΟΝ 24 .
Υπάρχουν τρία φυσικά μεγέθη που περιγράφουν της ένταση της ηλεκτρομαγνητικής ακτινοβολίας:
- η ένταση του ηλεκτρικού πεδίου, που μετράται σε V/m
- η ένταση του μαγνητικού πεδίου, που μετράται σε Α/m
- η πυκνότητα ισχύος που μετράται σε W/m².
Τα κινητά τηλέφωνα και οι σταθμοί βάσης εκπέμπουν ηλεκτρομαγνητική ακτινοβολία, δηλαδή ταλαντώσεις ηλεκτρικών και μαγνητικών πεδίων που διαδίδονται στο χώρο υπό τη μορφή κύματος μεταφέροντας ενέργεια. Τα διάφορα είδη της ηλεκτρομαγνητικής ακτινοβολίας διακρίνονται μεταξύ τους ανάλογα με τη συχνότητα ή το μήκος κύματος του διαδιδόμενου κύματος. Η συχνότητα και το μήκος κύματος είναι δύο αντιστρόφως ανάλογα μεγέθη, δηλαδή όσο μικρότερη συχνότητα έχουμε τόσο μεγαλύτερο είναι το μήκος κύματος.
Για τις εκπομπές ηλεκτρομαγνητικής ακτινοβολίας σύμφωνα με τη Σύσταση του Συμβουλίου της Ευρωπαϊκής Ένωσης “Σχετικά με τον περιορισμό της έκθεσης του κοινού σε ηλεκτρομαγνητικά πεδία 0 Hz – 300 GHz “, ( L 199,1999/519/ EC ) με την οποία θεσπίζονται βασικοί περιορισμοί ( basic restrictions ) και επίπεδα αναφοράς ( reference levels ) για τα επίπεδα ηλεκτρομαγνητικής ακτινοβολίας που επάγουν οι κεραίες αυτές. Το ελληνικό κράτος έχει θεσπίσει πιο αυστηρά όρια ασφαλούς έκθεσης συγκριτικά με τα όρια που έχει θεσπίσει η Ευρωπαϊκή Ένωση. Σύμφωνα με την Ελληνική Νομοθεσία εξασφαλίζεται ο τρόπος διενέργειας των μετρήσεων, καθορίζονται μηχανισμοί ελέγχου για τα επίπεδα H/M ακτινοβολίας καθώς και απαγορεύεται η εγκατάσταση κεραιών η οποία δεν έχει εγκριθεί από εξουσιοδοτημένους φορείς.
Η ακτινοβολούμενη ισχύς από μια κεραία προς μία κατεύθυνση δεν είναι σταθερή, αλλά μειώνεται πολύ γρήγορα συγκριτικά με την απόσταση. Η μείωση που υφίστανται η ακτινοβολούμενη ισχύς είναι αντίστροφη του τετραγώνου της απόστασης δηλαδή σε διπλάσια απόσταση προσπίπτει το ένα τέταρτο της ακτινοβολίας και σε δεκαπλάσια απόσταση το ένα εκατοστό.
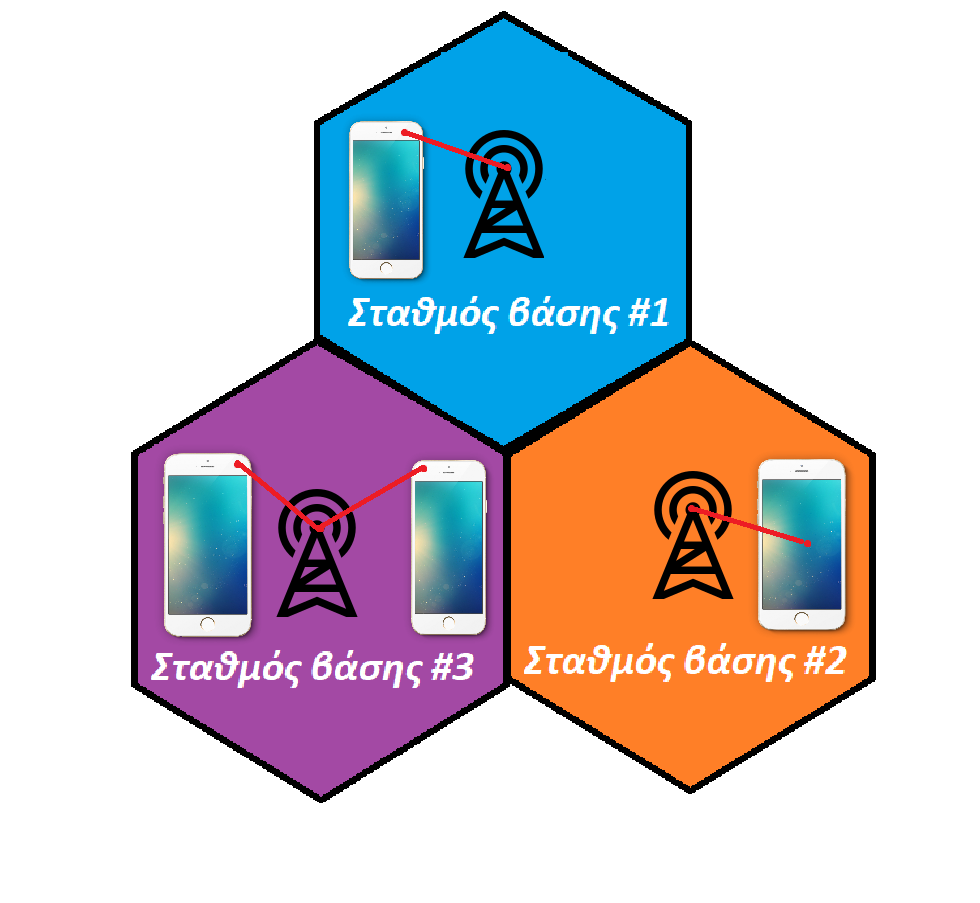
Το βασικό χαρακτηριστικό των Συστημάτων Κινητών Επικοινωνιών είναι η κυψελωτή δομή τους. Σε αυτή τη δομή βασίζεται η σχεδίαση των ραδιο-δικτύων. Κάθε κυψέλη εξυπηρετεί μέσω ενός σταθμού βάσης (Σ.Β.) μια γεωγραφική περιοχή ακτίνας από μερικά μέτρα ως κάποιες δεκάδες χιλιόμετρα. Οι Σ.Β. συνδέονται στα κέντρα μεταγωγής, που διασυνδέουν το ραδιο-δίκτυο με τα εξωτερικά δίκτυα φωνής και δεδομένων. Στους Σ.Β. κάθε κυψέλης αποδίδουμε μια ομάδα συχνοτήτων (διαύλων) και επιδιώκουμε να επαναχρησιμοποιούμε τους ίδιους διαύλους στο χώρο. Πυκνή επαναχρησιμοποίηση συνεπάγεται μεγάλη φασματική απόδοση αλλά και αύξηση των ανεπιθύμητων ομοδιαυλικών παρεμβολών.
Είναι μια κοινή λανθασμένη αντίληψη ότι για να επιτύχουμε διπλάσια απόσταση σε μια σύνδεση ραδιοκάλυψης, μπορούμε απλά να διπλασιάσουμε την ισχύ. Η πραγματικότητα είναι ότι για να διπλασιαστεί η απόσταση, απαιτείται 4 φορές η ισχύς μετάδοσης. Αυτός ο κανόνας προέρχεται από έναν απλό γεωμετρικό τύπο που αναφέρει ότι η διάδοση των ραδιοκυμάτων επεκτείνεται σε σχήμα σφαίρας και η επιφάνεια μιας σφαίρας (και επομένως πυκνότητας ισχύος) αλλάζει αναλογικά με το τετράγωνο της ακτίνας (στην περίπτωση αυτή η ακτίνα είναι η απόσταση).
Με απλά λόγια, εάν με έναν πομπό 1 Watt μπορούμε να καλύψουμε 1 χιλιόμετρο απόσταση, για να φτάσουμε τα 2 χιλιόμετρα θα χρειαστούμε έναν πομπό 4 Watt. Φυσικά η απόσταση ραδιοκάλυψης εξαρτάται όχι μόνο από την ισχύ ενός πομπού, αλλά και από το κέρδος και το ύψος της κεραίας, την ποιότητα του δέκτη και από τα εμπόδια στο έδαφος.
Τα θεσμοθετημένα όρια έχουν θεσπιστεί λαμβάνοντας υπόψιν τις αβεβαιότητες παραγόντων όπως περιβαλλοντικές συνθήκες αλλά και τις διαφορετικές καταστάσεις σωματικής ευεξίας του κοινού. Σύμφωνα με τα ελληνικά πρότυπα τα όρια αποτελούν το 70% των τιμών της Ε.Ε. και ειδικότερα για ευπαθείς ομάδες οι τιμές που προκύπτουν ανέρχονται στο 60% των αρχικών τιμών, διασφαλίζοντας την πλήρη ασφάλεια και την τήρηση της κείμενης νομοθεσίας σε όλη την ελληνική επικράτεια.
Η τεχνολογία του 5G είναι η μόνη διαθέσιμη τεχνολογία με την οποία ένας γιατρός σε αστικό περιβάλλον μπορεί να εξετάσει αξιόπιστα, με υψηλή ευκρίνεια και με χρήση συσκευών και ρομποτικών μηχανισμών να χειρουργήσει καθώς και να ψηλαφίσει τους ιστούς ενός ασθενούς που βρίσκεται σε ένα απομακρυσμένο νησί. Επίσης η τεχνολογία 5G είναι η μόνη που μπορεί να υποστηρίξει την τηλεδιάγνωση με χρήση έμπειρων συστημάτων τεχνητής νοημοσύνης.
Η Ψηφιοποίηση της Οικονομίας εξελίσσεται με γρήγορους ρυθμούς προσφέροντας αναγνωρισμένα οφέλη. Η ανάπτυξη δικτύων 5G είναι ο καταλύτης για την εμβάθυνση της Ψηφιακής Οικονομίας. Η δυνατότητα πρόσβασης σε νέες αγορές και η αύξηση του τμήματος του πληθυσμού στο οποίο απευθύνονται, η μείωση του κόστους παραγωγής και αύξησης της παραγωγικότητας καθώς και η δημιουργία προϋποθέσεων γρήγορης υιοθέτησης της καινοτομίας σε όλα τα στάδια των παραγωγικών τους διαδικασιών είναι μερικά από τα οφέλη που προκύπτουν.
Λόγω της παγκοσμιοποίησης της οικονομίας, κλάδοι και χώρες που κινούνται ταχύτερα προς την Ψηφιακή Οικονομία έχουν καθοριστικό για το μέλλον και τη βιώσιμη ανάπτυξη πλεονέκτημα έναντι των καθυστερημένων. Η ανάπτυξη της τεχνολογίας 5G μπορεί να αποτελέσει μοναδικό παράγοντα και πόλο ανάπτυξης και παραγωγής καινοτομίας και η Ελλάδα μόνο οφέλη μπορεί να έχει από μια έγκαιρη υιοθέτησή της. Μια αργή και παθητική υιοθέτηση του 5G μόνο αρνητικά αποτελέσματα μπορεί να έχει για τη χώρα, καθώς άλλοι (χώρες και κλάδοι) θα έχουν αποκτήσει πολύτιμη εμπειρία όσον αφορά στη γοργή και αποδοτική μετάβασή τους στην Ψηφιακή Οικονομία, τόσο μέσω της έγκαιρης ανάπτυξης νέων υπηρεσιών και περιπτώσεων χρήσης, όσο και μέσω της παραγωγής και εξαγωγής καινοτομίας.
Η ακτινοβολία από τα κινητά τηλέφωνα και τους σταθμούς βάσης δεν είναι ραδιενεργός. Αναφερόμαστε σε μη ιοντίζουσα Η/Μ ακτινοβολία η οποία δεν προκαλεί ιοντισμό των μορίων. Το ηλεκτρομαγνητικό φάσμα περιλαμβάνει τις εξής μη ιοντίζουσες Η/Μ ακτινοβολίες :
- Στατικά ηλεκτρικά και Μαγνητικά Πεδία που είναι αμετάβλητα (π.χ. το φυσικό μαγνητικό πεδίο της Γης)
- Ηλεκτρικά και Μαγνητικά πεδία της τάξεως των 50Hz (π.χ. ηλεκτρικές συσκευές, υποσταθμοί, γραμμές διανομής ηλεκτρικής ενέργειας)
- Ραδιοκύματα (π.χ. μετάδοση ραδιοφωνικών και τηλεοπτικών εκπομπών, ραντάρ)
- Φως
- Υπέρυθρη (π.χ σώματα με υψηλή θερμοκρασία)
- Υπεριώδη (π.χ. ήλιος)
